Multimodal Data Governance: A Comprehensive Approach to Business Transformation | Part 1
In today's data-driven landscape, businesses rely on multiple data sources, formats, and structures to drive decision-making and innovation. Traditional data governance models often struggle to manage the complexity of diverse data ecosystems, making Multimodal Data Governance (MDG) a critical approach for modern enterprises. MDG ensures the seamless integration, security, and compliance of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data across multiple platforms, enabling organizations to optimize their data assets effectively.
This blog will explore what Multimodal Data Governance is, how businesses can implement it, its key aspects, and its transformative impact on business operations.
What Is Multimodal Data Governance?
Multimodal Data Governance (MDG) refers to a governance framework designed to manage multiple types of data—structured (databases, spreadsheets), semi-structured (JSON, XML), and unstructured (images, videos, documents). As businesses operate in complex digital ecosystems, the need to govern data across cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments has become crucial.
Unlike traditional data governance, which primarily focuses on structured data, MDG provides a unified approach to governing diverse data types. This includes defining policies for data quality, security, lineage, access controls, and compliance across all data formats. With MDG, organizations can break down data silos, ensure compliance with regulatory standards, and enhance operational efficiency.
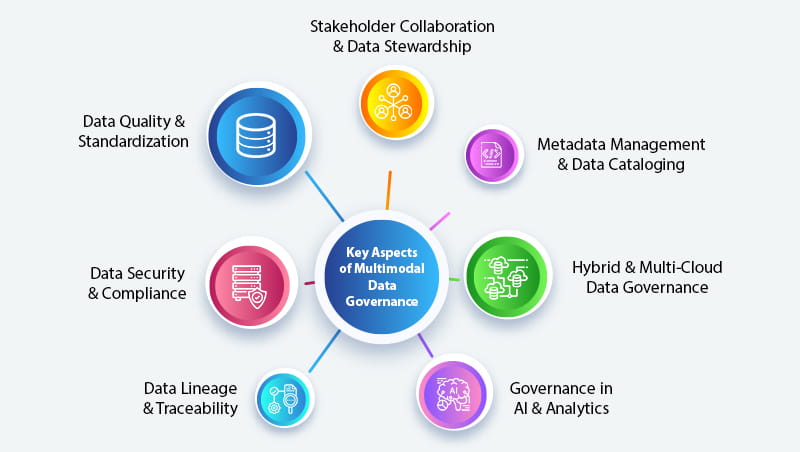
Key Aspects of Multimodal Data Governance
Implementing Multimodal Data Governance (MDG) involves several critical aspects that ensure data integrity, security, compliance, and usability across different data formats and environments. By addressing these key elements, businesses can effectively govern structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, making it more accessible and reliable for decision-making.
Data Quality & Standardization
Ensuring data quality is fundamental to effective data governance. Since multimodal data originates from diverse sources—including databases, IoT devices, social media, and enterprise applications—inconsistencies and redundancies often arise. Organizations must implement:
- Automated data cleansing to remove duplicate, incomplete, or incorrect records.
- Standardized data formats to improve interoperability between different data sources.
- Data validation rules to ensure accuracy and consistency across all platforms.
By maintaining high data quality standards, businesses can improve analytics, enhance decision-making, and build trust in data-driven insights.
Data Security & Compliance
With increasing cyber threats and stringent data privacy regulations, securing multimodal data is a top priority. Unlike structured data, semi-structured and unstructured data—such as emails, documents, and multimedia files—are more vulnerable to security risks. Organizations should enforce:
- End-to-end encryption for data at rest, in transit, and in use.
- Role-based and attribute-based access controls (RBAC & ABAC) to prevent unauthorized data access.
- Regulatory compliance frameworks (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, ISO 27001) to meet industry-specific legal requirements.
Strong data security and compliance measures ensure that businesses protect sensitive information, maintain customer trust, and avoid hefty penalties.
Data Lineage & Traceability
Understanding where data comes from, how it changes over time, and how it is used is essential for maintaining governance integrity. Data lineage and traceability provide visibility into data movement across various systems and processes. Key practices include:
- Automated data lineage tracking to monitor how data flows through databases, applications, and analytics platforms.
- Data provenance management to ensure authenticity and reliability of critical business data.
- Version control and change tracking to audit modifications and detect potential governance issues.
With strong data lineage and traceability, organizations can enhance data transparency, support compliance audits, and improve troubleshooting capabilities.
Governance in AI & Analytics
As businesses integrate Artificial Intelligence (AI) and advanced analytics into their operations, governing AI-driven data becomes essential. AI models rely on diverse data sources, and poorly governed data can lead to biased insights, inaccurate predictions, and compliance risks. To ensure responsible AI usage, organizations should:
- Implement data governance policies for AI training datasets to reduce bias and ensure ethical AI development.
- Monitor and audit AI-driven insights to detect anomalies and inconsistencies.
- Establish explainability frameworks to ensure AI decisions are transparent and interpretable.
By embedding governance into AI workflows, businesses can leverage data-driven intelligence responsibly and enhance trust in AI-powered solutions.
Hybrid & Multi-Cloud Data Governance
Modern enterprises operate in hybrid and multi-cloud environments, making data governance across different cloud providers and on-premise systems a complex challenge. To ensure consistency and control, organizations should:
- Adopt a unified governance framework that applies policies across on-premises, private cloud, and public cloud platforms.
- Utilize cloud-native governance tools (e.g., Azure Purview, AWS Lake Formation, Google Data Catalog) to monitor and manage data assets efficiently.
- Implement data sovereignty policies to comply with regional data privacy laws and cross-border data transfer regulations.
With an effective hybrid and multi-cloud governance approach, businesses can seamlessly manage data security, accessibility, and compliance across all digital environments.
Metadata Management & Data Cataloging
Metadata- the descriptive information about data- plays a crucial role in data discoverability and governance. A well-structured data catalog enables organizations to:
- Improve data searchability by tagging datasets with metadata attributes such as source, format, and usage.
- Enhance data governance automation through AI-driven metadata classification.
- Enable data lineage tracking by linking metadata with governance policies and compliance rules.
By integrating metadata management with data governance frameworks, organizations can streamline data access, boost operational efficiency, and foster data-driven innovation.
Stakeholder Collaboration & Data Stewardship
Successful Multimodal Data Governance requires cross-functional collaboration between IT teams, compliance officers, data analysts, and business leaders. Organizations should:
- Appoint Data Stewards to oversee governance policies and ensure adherence to best practices.
- Establish governance committees to define and enforce data policies.
- Promote data literacy across departments to encourage responsible data handling and usage.
With a well-structured governance culture, businesses can maximize data value, reduce governance-related risks, and ensure regulatory compliance across the organization.
How Can Data Governance Be Implemented in Multimodal Data Governance?
Implementing Multimodal Data Governance (MDG) requires a strategic approach that ensures the management, security, compliance, and accessibility of diverse data types across an organization. Unlike traditional data governance, which primarily focuses on structured data, MDG extends its scope to semi-structured and unstructured data, making implementation more complex but crucial for modern businesses.
Here’s a step-by-step approach to effectively implementing data governance in a multimodal data environment:
Data Classification & Cataloging
Before governance policies can be enforced, businesses must classify and catalog their data assets. This step involves:
- Identifying structured (databases), semi-structured (XML, JSON), and unstructured (videos, images, PDFs) data.
- Assigning metadata tags to ensure proper data organization.
- Implementing data discovery tools to create an enterprise-wide data catalog for accessibility and compliance tracking.
This step helps businesses understand what data they have, where it resides, and how it can be governed effectively.
Establishing Policy-Driven Data Management
A strong policy framework is critical for ensuring data security, compliance, and governance across all data types. Organizations should:
- Define data governance policies for access control, retention, security, and compliance based on regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA.
- Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) and attribute-based access controls (ABAC) to prevent unauthorized data usage.
- Enforce data retention and deletion policies to comply with industry standards and reduce data clutter.
By creating clear policies, businesses ensure that data is handled securely and ethically across all platforms.
AI & Automation for Data Governance
With the increasing volume and complexity of data, manual governance processes are no longer effective. Businesses must leverage AI and automation to:
- Implement AI-driven metadata management for automated classification and tagging.
- Use machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies and potential data governance violations.
- Automate data lineage tracking to monitor how data moves and transforms across different systems.
AI and automation help businesses maintain governance consistency, improve data quality, and enhance compliance monitoring.
Interoperability & Integration of Governance Frameworks
Since businesses use multiple storage systems, databases, and cloud platforms, integrating governance frameworks across hybrid and multi-cloud environments is essential. This involves:
- Adopting API-driven governance solutions that allow interoperability between different data management systems.
- Ensuring governance policies are consistently applied across on-premise, cloud, and SaaS environments.
- Using federated data governance models to govern data across distributed architectures without centralizing everything in one location.
By ensuring seamless integration, businesses can enforce governance policies across all data repositories efficiently.
Stakeholder Collaboration & Data Stewardship
Effective data governance requires the involvement of multiple stakeholders, including IT teams, compliance officers, business leaders, and data stewards. To establish a governance-driven culture, organizations should:
- Appoint Data Stewards and Data Owners who oversee data governance policies and enforce best practices.
- Train employees on data governance policies, compliance requirements, and security measures.
- Encourage cross-functional collaboration to align governance strategies with business objectives.
A governance framework is only as strong as its adoption—a well-trained workforce ensures governance policies are followed consistently.
Implementing Continuous Monitoring & Compliance Audits
Governance is not a one-time activity; it requires continuous monitoring and regular compliance audits to ensure ongoing adherence. Organizations should:
- Deploy real-time monitoring tools that track data usage, security breaches, and unauthorized access.
- Conduct regular audits to evaluate compliance with governance policies and regulatory standards.
- Use data governance dashboards and analytics to measure governance effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Regular monitoring ensures that governance remains up to date and adaptable to new regulations and business needs.
Conclusion
In an era where data is a key driver of business success, Multimodal Data Governance provides enterprises with the foundation to manage, secure, and utilize diverse data types effectively. By implementing structured governance policies, AI-driven automation, and compliance measures, businesses can unlock the full potential of their data while ensuring regulatory adherence.
Stay tuned for Part 2, where we’ll explore the challenges, benefits, and how Espire helps businesses implement Multimodal Data Governance successfully. Till then connect with us and explore how Espire can help your business achieve exponential data governance across your organization.

