The Evolution from Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to Cognitive Automation: What’s Next?
Automation has been a game-changer for businesses, streamlining processes and improving operational efficiency. Initially, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) paved the way by automating rule-based, repetitive tasks. However, the business landscape is evolving, and so are the demands for more advanced technologies. Cognitive automation is the next step in this journey, bringing the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into automation. In this blog, we’ll explore the shift from RPA to cognitive automation, what this evolution means for businesses, and what lies ahead.
Automation has long been a key driver of business transformation. According to recent reports, the global Robotic Process Automation (RPA) market is projected to grow from $2.5 billion in 2022 to over $24.6 billion by 2033, indicating the continued demand for automation technologies. However, while RPA has been successful in streamlining repetitive tasks, it is now reaching its limitations as businesses face increasingly complex challenges that require more than just rule-based automation.
The market is witnessing a shift towards cognitive automation, which incorporates advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to handle more sophisticated tasks. The cognitive automation market is expected to grow rapidly, fueled by increasing adoption across industries such as finance, healthcare, and customer service.
Understanding RPA: A Foundation for Automation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has been instrumental in simplifying business operations. It works by mimicking human actions to execute structured tasks, such as data entry, form filling, and generating reports. These tasks are typically repetitive, time-consuming, and rule-based, making RPA the perfect solution.
The Limitations of RPA: Why a Shift Was Necessary
While Robotic Process Automation (RPA) revolutionized business operations by automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, its limitations soon became apparent. RPA relies heavily on structured data and predefined workflows, which restricts its ability to adapt to dynamic, unstructured processes. As businesses became more complex, so did the need for automation that could handle more than just repetitive tasks. This gap between task automation and intelligent process management led to the demand for a more advanced solution- cognitive automation.
RPA could not interpret unstructured data, such as images, emails, or audio, and it lacked decision-making capabilities. As a result, many processes still required human intervention to interpret and analyze data before moving forward in a workflow. This reliance on humans for higher-order tasks created bottlenecks, driving the need for a technology that could handle both routine and complex tasks seamlessly.
What Makes Cognitive Automation Different?
Cognitive automation builds on the foundation of traditional Robotic Process Automation (RPA) by integrating advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP). While RPA focuses on automating structured, rule-based tasks, cognitive automation goes beyond by enabling systems to handle unstructured data, make decisions, and continuously improve through learning. Two core elements that set cognitive automation apart from RPA are Knowledge Representation and Reasoning (KRR) and Computer Vision (CV), both of which empower automation to simulate human-like intelligence in decision-making and data interpretation.
Knowledge Representation and Reasoning (KRR): Learning from Experience
One of the most transformative aspects of cognitive automation is its ability to make decisions based on prior experiences, much like how humans learn and evolve over time. This is achieved through Knowledge Representation and Reasoning (KRR), a fundamental AI technique that allows machines to represent data in a way that is meaningful for decision-making.
KRR operates on two levels:
- Representation: This refers to how data is stored and structured within the system. In cognitive automation, data isn’t just processed based on predefined rules; it is represented in ways that allow the system to understand the relationships between different data points.
- Reasoning: Reasoning is the decision-making aspect, where the system uses the stored data to make inferences and solve problems. Cognitive automation, powered by KRR, can analyze past data and experiences to make informed decisions, offering a level of adaptability and intelligence that RPA lacks.
This capacity for KRR allows cognitive automation to simulate human-like cognitive abilities, enabling systems to evolve and respond to dynamic situations without needing constant reprogramming.
Computer Vision (CV): Understanding Non-Digital Data
Another critical technology that differentiates cognitive automation from RPA is Computer Vision (CV). While traditional RPA can only handle structured, digital data, cognitive automation leverages CV to interpret and extract information from images, videos, and text that are not in a structured digital format.
Computer Vision is a form of AI that enables machines to "see" and analyze visual content such as scanned documents, photographs, or even videos.
By enabling automation systems to interact with unstructured visual data, CV expands the range of tasks cognitive automation can handle. This makes it a game-changer for industries that rely heavily on processing physical or unstructured content, such as healthcare, manufacturing, and legal services.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) in Cognitive Automation
One of the standout features of cognitive automation is its ability to process natural language, thanks to NLP. Natural Language Processing enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. This has opened new possibilities for automating complex tasks like customer service, where understanding context and responding appropriately are critical.
NLP allows cognitive automation to read and understand emails, analyze customer sentiment, and engage in conversations via chatbots, all of which go beyond the capabilities of traditional RPA. With NLP, businesses can automate tasks that involve high levels of human interaction, such as handling customer queries, processing feedback, and even performing content analysis. This has made cognitive automation an essential tool for improving customer experiences.
Machine Learning: Enabling Continuous Improvement
At the core of cognitive automation’s adaptability is machine learning (ML), which allows automation systems to continuously improve and become more efficient over time. Unlike RPA, which requires explicit programming for every task, cognitive automation uses ML algorithms to learn from historical data, identify patterns, and make predictions based on previous interactions.
For example, in financial services, cognitive automation systems can learn from past transactions to detect anomalies and flag potential fraud. In healthcare, ML models can analyze vast amounts of patient data to provide better diagnostic recommendations. The ability to improve and adapt to changing circumstances without manual intervention makes cognitive automation a highly valuable asset for businesses looking for scalability and efficiency.
The Integration of AI and Machine Learning in Automation
The primary driver of cognitive automation is the integration of AI and machine learning into automation systems. This integration allows cognitive automation to learn from historical data, improve decision-making accuracy, and predict outcomes, something RPA alone cannot achieve.
How AI Enhances Automation Beyond Rule-Based Systems
Traditional automation, such as RPA, follows predefined rules to complete tasks. While effective for structured, repetitive processes, it lacks the flexibility to adapt to unpredictable scenarios. Artificial Intelligence (AI) enhances automation by bringing in the ability to make decisions based on real-time data, context, and learning from previous outcomes.
AI allows automation systems to analyze data in-depth, understand patterns, and apply contextual understanding. This means AI can perform tasks that require judgment, such as fraud detection, personalized marketing, and customer sentiment analysis. Unlike rule-based systems that require reprogramming for every change, AI-powered automation can adapt and evolve as it gathers more data, leading to smarter, more efficient processes.
Predictive Analytics: Unlocking Business Insights
One of the most valuable applications of AI and machine learning in automation is predictive analytics. By analyzing historical data, machine learning algorithms can predict future outcomes, trends, and behaviors. This capability allows businesses to make proactive decisions, optimizing operations and mitigating risks.
For instance, in supply chain management, predictive analytics can forecast demand fluctuations, helping companies manage inventory more effectively. In healthcare, predictive models can anticipate patient needs or potential health risks based on medical history, enabling preventive care. The integration of AI-driven predictive analytics into automation empowers businesses to operate more strategically and efficiently.
AI-Driven Decision Making: The Future of Autonomous Systems
AI and machine learning enable cognitive automation to go beyond process automation and into the realm of autonomous decision-making. As machine learning models become more sophisticated, they can not only recommend actions but also autonomously execute them. This AI-driven decision-making is transforming industries like finance, manufacturing, and customer service.
In finance, AI can automate investment strategies by analyzing market data in real-time and executing trades based on predictive models. In manufacturing, AI-driven robots can optimize production schedules and manage supply chains with minimal human oversight. As businesses increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, AI-driven automation will become central to maintaining a competitive edge in the future.
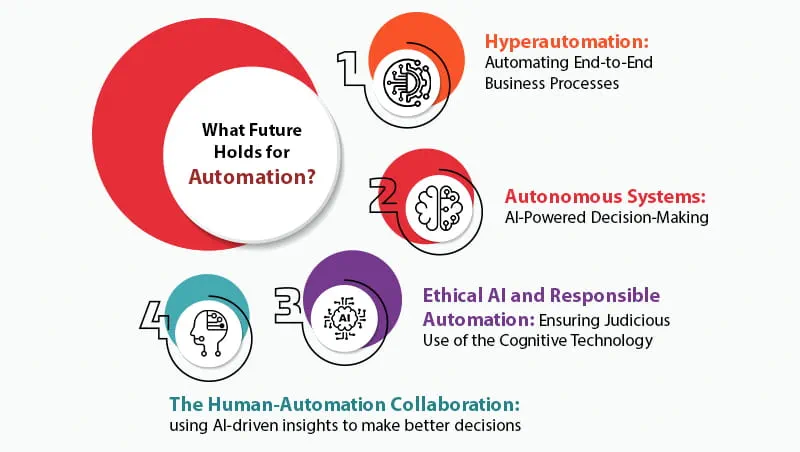
The Future of Automation: What’s Next?
As cognitive automation continues to advance, the possibilities for its application and impact on business operations are expanding rapidly. The future of automation will be shaped by the integration of more sophisticated AI technologies, the convergence of various automation tools, and the drive for increased autonomy in decision-making processes. Let’s explore some of the key trends and innovations that are set to define the future of automation.
Hyperautomation: Automating End-to-End Business Processes
One of the most significant trends in the future of automation is hyperautomation, which combines Robotic Process Automation (RPA), cognitive automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and other advanced technologies to automate entire business processes from start to finish. Hyperautomation enables businesses to move beyond the automation of individual tasks and towards the automation of complete workflows.
For instance, hyperautomation can automate the customer onboarding process in financial services, from verifying documents and checking compliance to approving applications and generating reports. It creates a seamless flow across multiple systems and departments, reducing bottlenecks and increasing operational efficiency. As hyperautomation evolves, businesses will rely more heavily on interconnected systems that can manage complex workflows with minimal human intervention.
Autonomous Systems: AI-Powered Decision-Making
As AI technologies become more advanced, automation systems will gain greater autonomy, enabling them to make decisions without human oversight. Autonomous systems represent the next leap in automation, where machines and AI-powered algorithms can not only execute tasks but also independently decide how to perform them based on real-time data and predictive analytics.
In industries like manufacturing, autonomous robots can optimize production schedules, monitor equipment for maintenance needs, and even troubleshoot issues on their own. In finance, AI systems are already making real-time trading decisions based on complex market data. As these systems become more refined, they will reshape how businesses operate, allowing for faster, data-driven decision-making at scale.
Ethical AI and Responsible Automation
With the growing use of AI in automation comes the need for more robust ethical guidelines and governance frameworks. As cognitive automation systems take on more decision-making responsibilities, ensuring that these systems operate ethically, transparently, and without bias will be crucial.
Businesses will need to implement strong AI governance policies that address issues such as data privacy, algorithmic transparency, and accountability for AI-driven decisions. The development of responsible AI practices will ensure that automation benefits society at large while minimizing potential risks associated with autonomous decision-making.
The Human-Automation Collaboration
Despite the rise of cognitive and autonomous systems, the future of automation is not about replacing humans but rather enhancing human capabilities through collaboration with AI. As machines take over repetitive and complex tasks, human workers will be freed to focus on more strategic, creative, and problem-solving roles that require emotional intelligence and critical thinking.
Automation will allow employees to work alongside intelligent systems, using AI-driven insights to make better decisions, improve customer experiences, and innovate faster. This symbiotic relationship between humans and machines will redefine the workplace, enabling businesses to thrive in an increasingly digital and automated world.
Conclusion
The shift from Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to cognitive automation marks a significant milestone in the automation journey. While RPA revolutionized how businesses handle repetitive tasks, cognitive automation is enabling companies to tackle more complex processes with the help of AI and machine learning. As businesses continue to adopt cognitive automation, they will unlock new opportunities for efficiency, innovation, and growth.
The future of automation lies in the ability to not only perform tasks but also think, learn, and adapt, making cognitive automation a powerful tool for businesses looking to stay competitive in an increasingly digital world.

